Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 61
Propose structures and draw condensed formulas of the three isomers with the formula C3H8O.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of isomers. Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structural arrangements. In this case, we are looking for structural isomers of C3H8O.
Step 2: Identify the possible functional groups. With the formula C3H8O, the compound could be an alcohol (R-OH) or an ether (R-O-R').
Step 3: Draw the first isomer as an alcohol. Start with a straight chain of three carbon atoms (propane) and attach an -OH group to one of the carbon atoms to form 1-propanol.
Step 4: Draw the second isomer as another alcohol. Rearrange the -OH group to a different carbon atom in the chain to form 2-propanol, ensuring the carbon chain remains intact.
Step 5: Draw the third isomer as an ether. Consider the possibility of an ether by having two carbon groups attached to an oxygen atom, such as methoxyethane (CH3-O-CH2-CH3).
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Isomerism
Isomerism refers to the phenomenon where compounds with the same molecular formula exhibit different structural or spatial arrangements. In the case of C3H8O, isomers can differ in the connectivity of atoms or the arrangement of functional groups, leading to distinct chemical properties and behaviors.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Isomerism in Coordination Complexes Example
Structural Formulas
Structural formulas represent the arrangement of atoms within a molecule, showing how atoms are bonded to each other. For isomers of C3H8O, drawing condensed formulas involves illustrating the connectivity of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, which helps in visualizing the different isomeric forms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
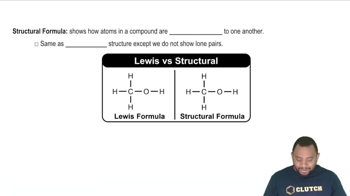
Structural Formula
Functional Groups
Functional groups are specific groups of atoms within molecules that determine the chemical reactivity and properties of those molecules. In the context of C3H8O, identifying functional groups such as alcohols (–OH) or ethers (R–O–R') is crucial for distinguishing between the isomers and understanding their chemical behavior.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Carbonyl Functional Groups
Related Practice
