Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 62
If someone reported the preparation of a compound with the formula C3H9, most chemists would be skeptical. Why?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the concept of valency and bonding in carbon atoms. Carbon typically forms four covalent bonds due to its four valence electrons.
Step 2: Analyze the given molecular formula C3H9. Calculate the total number of hydrogen atoms that can bond with three carbon atoms, considering each carbon can form four bonds.
Step 3: Consider the possible structures for C3H9. Start by arranging three carbon atoms in a chain or branched structure and attempt to satisfy the valency of each carbon with hydrogen atoms.
Step 4: Realize that for three carbon atoms, the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be bonded is eight, forming propane (C3H8). This is because each carbon atom can only form four bonds.
Step 5: Conclude that the formula C3H9 is not feasible because it suggests an extra hydrogen atom that cannot be accommodated without violating the valency rules of carbon, leading to skepticism among chemists.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
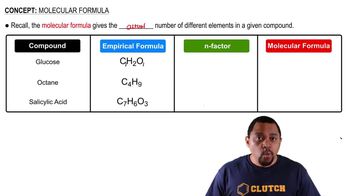
Molecular Formula and Valency
A molecular formula represents the number and type of atoms in a molecule. In the case of C3H9, the formula suggests a compound with three carbon atoms and nine hydrogen atoms. However, carbon typically forms four bonds (valency of four), and with three carbons, the maximum number of hydrogen atoms that can be bonded is eight (C3H8), making C3H9 unlikely.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Determining Molecular Formulas
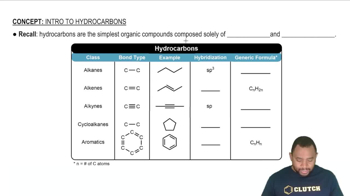
Hydrocarbon Structure
Hydrocarbons are organic compounds consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen. They can be classified as alkanes, alkenes, or alkynes based on the types of bonds between carbon atoms. C3H9 does not fit the structure of a stable alkane, which follows the formula CnH2n+2, indicating that it cannot exist as a stable compound under normal conditions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Intro To Hydrocarbons
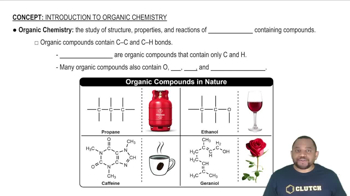
Stability of Organic Compounds
The stability of organic compounds is influenced by their ability to satisfy the octet rule, where atoms seek to have eight electrons in their outer shell. A compound like C3H9 would likely have an unstable structure due to excessive hydrogen atoms, leading to a high degree of strain or reactivity, which is why chemists would be skeptical about its existence.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
Related Practice
