Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 94
Jojoba wax, used in candles and cosmetics, is partially composed of the ester of stearic acid and a straight-chain C22 alcohol. Draw the structure of this ester.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand the components involved in the ester formation. An ester is formed from the reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. In this case, the carboxylic acid is stearic acid, and the alcohol is a straight-chain C22 alcohol.
Step 2: Write the structure of stearic acid. Stearic acid is a saturated fatty acid with the chemical formula C18H36O2. Its structure consists of a long hydrocarbon chain (17 CH2 groups) ending with a carboxylic acid group (COOH).
Step 3: Write the structure of the straight-chain C22 alcohol. This alcohol has 22 carbon atoms in a straight chain, with a hydroxyl group (OH) at one end. Its general formula is C22H45OH.
Step 4: Form the ester linkage. In an esterification reaction, the hydroxyl group (OH) from the carboxylic acid and the hydrogen (H) from the alcohol's hydroxyl group are removed to form water (H2O), and the remaining oxygen from the alcohol forms a bond with the carbonyl carbon of the acid, creating an ester linkage (COO).
Step 5: Draw the complete structure of the ester. Combine the remaining parts of stearic acid and the C22 alcohol through the ester linkage. The resulting structure will have the long hydrocarbon chain of the alcohol connected to the carbonyl carbon of the stearic acid, forming the ester bond (RCOOR').
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ester Formation
Ester formation is a chemical reaction between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid, resulting in the production of an ester and water. This process, known as esterification, typically involves the removal of a water molecule as the hydroxyl group (-OH) from the acid and a hydrogen atom from the alcohol combine. Understanding this reaction is crucial for drawing the structure of the ester in question.
Recommended video:
Guided course
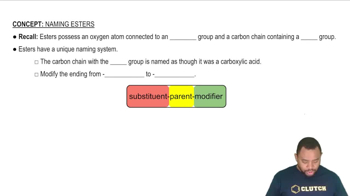
Rules for Naming Esters
Fatty Acids
Fatty acids are carboxylic acids with long hydrocarbon chains, which can be saturated or unsaturated. Stearic acid, a saturated fatty acid with an 18-carbon chain, is commonly used in the formation of esters. Recognizing the structure and properties of fatty acids is essential for accurately depicting the ester derived from stearic acid in the question.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Binary Acids
Long-Chain Alcohols
Long-chain alcohols are organic compounds with a hydroxyl (-OH) group attached to a long hydrocarbon chain. In this case, the straight-chain C22 alcohol contributes to the ester structure. Understanding the characteristics of long-chain alcohols, including their physical properties and how they interact with fatty acids, is vital for constructing the correct ester structure.
Recommended video:
Guided course
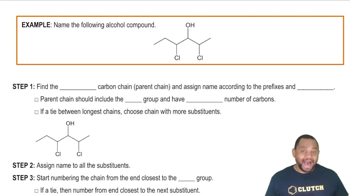
Naming Alcohols Example
Related Practice
