Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 57
Give line drawings for each of the following molecular formulas. You may have to use rings and/or multiple bonds in some instances. (b) C4H8 (c) C2H4O (d) CH2O2
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Understand that line drawings, also known as skeletal structures, represent organic molecules where carbon atoms are implied at the ends and intersections of lines, and hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are not shown explicitly.
Step 2: For C4H8, recognize that this formula can represent several isomers. Consider drawing structures with different arrangements of carbon atoms, such as a straight chain with a double bond (butene) or a ring structure (cyclobutane).
Step 3: For C2H4O, identify that this formula can represent compounds like acetaldehyde or ethylene oxide. Draw a structure with a carbonyl group (C=O) for acetaldehyde or an epoxide ring for ethylene oxide.
Step 4: For CH2O2, consider the possibility of different functional groups. This formula can represent formic acid or methanediol. Draw a structure with a carboxylic acid group (COOH) for formic acid or a diol structure for methanediol.
Step 5: Review each structure to ensure that the number of hydrogen atoms and the types of bonds (single, double, or rings) are consistent with the given molecular formulas.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
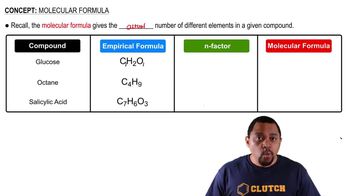
Molecular Formula
A molecular formula represents the number and types of atoms in a molecule, indicating the specific elements and their quantities. For example, C4H8 indicates a molecule containing four carbon atoms and eight hydrogen atoms. Understanding molecular formulas is essential for drawing structural representations, as they provide the foundational information needed to visualize the arrangement of atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Determining Molecular Formulas
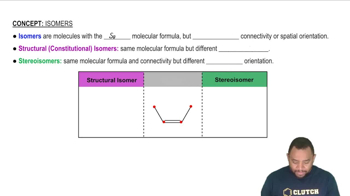
Structural Isomers
Structural isomers are compounds that share the same molecular formula but differ in the connectivity of their atoms. For instance, C4H8 can exist as different isomers, such as butene and cyclobutane, which have distinct structures and properties. Recognizing the potential for isomerism is crucial when drawing line structures, as it influences the arrangement of atoms and bonds.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Isomers
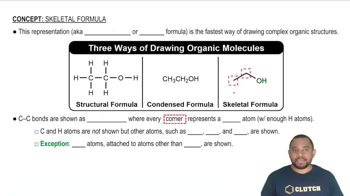
Line Drawings (Skeletal Structures)
Line drawings, or skeletal structures, are a simplified way to represent organic molecules, where carbon atoms are implied at the ends and intersections of lines. Hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are often omitted for clarity. This method allows chemists to easily visualize complex molecules, including rings and multiple bonds, which are essential for accurately depicting the structure of compounds like C2H4O and CH2O2.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Skeletal Formula
Related Practice
