Ch.23 - Organic and Biological Chemistry

Chapter 23, Problem 58
Provide a line drawing and the molecular formula for the following: (a) A linear alkyne with three carbon atoms and one triple bond, (b) A linear alkene with four carbon atoms and one double bond, (c) A cyclic alkene with five carbon atoms in a ring and two double bonds.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the structure of the linear alkyne with three carbon atoms. An alkyne is a hydrocarbon with at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. For three carbon atoms, the structure is HC≡C-CH₃, and the molecular formula is C₃H₄.
Step 2: Draw the line structure for the linear alkyne. In line structures, each vertex represents a carbon atom, and lines represent bonds. For HC≡C-CH₃, draw a line with three vertices, with a triple bond between the first two vertices.
Step 3: Identify the structure of the linear alkene with four carbon atoms. An alkene is a hydrocarbon with at least one carbon-carbon double bond. For four carbon atoms, the structure is CH₂=CH-CH₂-CH₃, and the molecular formula is C₄H₈.
Step 4: Draw the line structure for the linear alkene. For CH₂=CH-CH₂-CH₃, draw a line with four vertices, with a double bond between the first two vertices.
Step 5: Identify the structure of the cyclic alkene with five carbon atoms and two double bonds. A cyclic alkene is a ring structure with at least one double bond. For five carbon atoms, the structure is cyclopentadiene, with the molecular formula C₅H₆.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Alkynes
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain at least one carbon-carbon triple bond. They follow the general formula CnH2n-2, where 'n' is the number of carbon atoms. In the case of a linear alkyne with three carbon atoms, the molecular formula would be C3H4, and its structure would show a straight chain with a triple bond between the first and second carbon atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
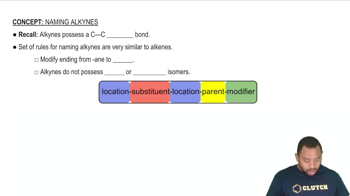
Rules for Naming Alkynes
Alkenes
Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons characterized by at least one carbon-carbon double bond. They adhere to the general formula CnH2n, indicating that for every 'n' carbon atoms, there are '2n' hydrogen atoms. For a linear alkene with four carbon atoms, the molecular formula is C4H8, and the structure will depict a straight chain with a double bond between two of the carbon atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
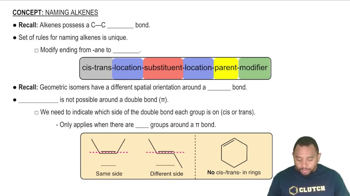
Rules for Naming Alkenes
Cyclic Alkenes
Cyclic alkenes are alkenes that form a ring structure and contain at least one double bond. The general formula for cyclic alkenes is CnH2n-2, similar to that of alkynes, but they differ in structure. For a cyclic alkene with five carbon atoms and two double bonds, the molecular formula would be C5H6, and the structure would illustrate a five-membered ring with two double bonds positioned between the carbon atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Rules for Naming Cyclic Alkanes
Related Practice
