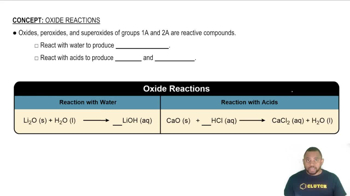
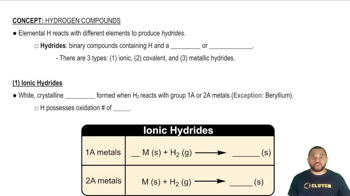
Ionic vs. Covalent Hydrides
Hydrides can be classified as ionic or covalent based on the type of bonding present. Ionic hydrides are formed between metals and hydrogen, characterized by the transfer of electrons, while covalent hydrides involve the sharing of electrons between nonmetals and hydrogen. The nature of the hydride formed is influenced by the element's electronegativity and its bonding characteristics, which are often indicated by the type of oxide it forms.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance