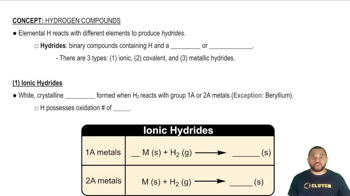
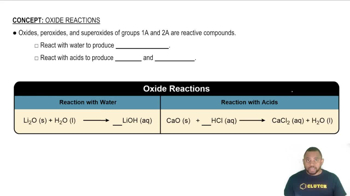
Acidic vs. Basic Oxides
Oxides can be classified as acidic, basic, or amphoteric based on their behavior in reactions with acids and bases. Basic oxides, often formed by metals, react with acids to produce salts and water, while acidic oxides, typically formed by nonmetals, react with bases. The classification is crucial for predicting the behavior of oxides formed by elements that also form ionic hydrides.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance