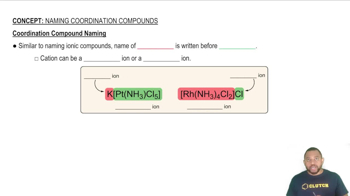
For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(a) [CrF6]3-
(b) [V(H2O)6]3+
(c) [Fe(CN)6]3-

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(a) [CrF6]3-
(b) [V(H2O)6]3+
(c) [Fe(CN)6]3-
Which of the following complexes are paramagnetic?
(a) [Mn(CN)6]3-
(b) [Zn(NH3)4]2+ (tetrahedral)
(c) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(d) [FeF6]4-
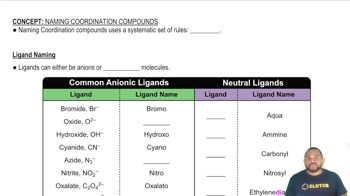
Draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following.
(a) [Cu(en)3]2+
(b) [FeF6]2-
(c) [Co(en)3]3+ (low spin)
Look at the colors of the isomeric complexes in Figure 21.12, and predict which is the stronger field ligand, nitro (-NO2) of nitrito (-ONO). Explain.
The amount of paramagnetism for a first-series transition metal complex is related approximately to its spin-only magnetic moment. The spin-only value of the magnetic moment in units of Bohr magnetons (BM) is given by sqrt(n(n + 2)), where n is the number of unpaired electrons. Calculate the spin-only value of the magnetic moment for the 2+ ions of the first-series transition metals (except Sc) in octahedral complexes with (a) weak-field ligands and (b) strong-field ligands. For which electron configurations can the magnetic moment distinguish between high-spin and low-spin electron configurations?
What hybrid orbitals are used by the metal ion and how many unpaired electrons are present the complex ion [VCl4]- with tetrahedral geometry?
(a) sp3; 2 unpaired electrons
(b) sp3; 3 unpaired electrons
(c) sp3d2; 3 unpaired electrons
(d) sp3d2; 4 unpaired electrons