Based on effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Fe2+
(d) Mn2+

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.85a
Problem 21.85a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Based on effective nuclear charge (Zeff), which ion is the strongest oxidizing agent?
(a) Cu2+
(b) Ni2+
(c) Fe2+
(d) Mn2+
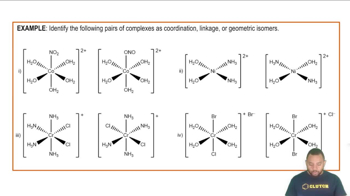
What is the systematic name for each of the following coordination compounds?
(a) Cs[FeCl4]
(b) [V(H2O)6](NO3)3
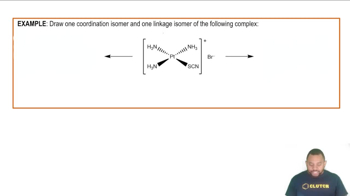
Nickel(II) complexes with the formula NiX2L2, where X− is Cl− or N-bonded NCS− and L is the monodentate triphenylphosphine ligand P(C6H5)3, can be square planar or tetrahedral.
(a) Draw crystal field energy-level diagrams for a square planar and a tetrahedral nickel(II) complex, and show the population of the orbitals.
For each of the following complexes, describe the bonding using valence bond theory. Include orbital diagrams for the free metal ion and the metal ion in the complex. Indicate which hybrid orbitals the metal ion uses for bonding, and specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(a) [AuCl4]2 (square planar)
What is the systematic name for each of the following ions?
(a) [MnCl4]2-
(b) [Ni(NH3)6]2+
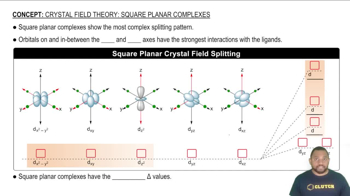
For each of the following complexes, draw a crystal field energy-level diagram, assign the electrons to orbitals, and predict the number of unpaired electrons.
(a) [Pt(NH3)4]2+ (square planar)