Cobalt(III) trifluoroacetylacetonate, Co(tfac)3, is a sixc oordinate, octahedral metal chelate in which three planar, bidentate tfac ligands are attached to a central Co atom:
(a) Draw all possible diastereoisomers and enantiomers of Co(tfac)3.

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.79a
Problem 21.79a Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Cobalt(III) trifluoroacetylacetonate, Co(tfac)3, is a sixc oordinate, octahedral metal chelate in which three planar, bidentate tfac ligands are attached to a central Co atom:
(a) Draw all possible diastereoisomers and enantiomers of Co(tfac)3.
There are two possible [M(OH)4]- complexes of first-series transition metals that have three unpaired electrons.
(a) What are the oxidation state and the identity of M in these complexes?
(b) Using orbital diagrams, give a valence bond description of the bonding in each complex.
(c) Based on common oxidation states of first-series transition metals (Figure 21.6), which [M(OH)4]- complex is more likely to exist?
<QUESTION REFERENCES FIGURE 21.6>-
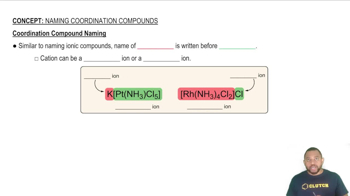
Tell how many diastereoisomers are possible for each of the following complexes, and draw their structures.
(a) Pt(NH3)3Cl (square planar)
(b) [FeBr2Cl2(en)]-
Two first-series transition metals have three unpaired electrons in complex ions of the type [MCl4]2-.
(a) What are the oxidation state and the identity of M in these complexes?
(b) Draw valence bond orbital diagrams for the two possible ions.
(c) Based on common oxidation states of first-series transition metals (Figure 21.6), which ion is more likely to exist?
<QUESTION REFERENCES FIGURE 21.6>
Constitutional isomers of a ruthenium(II) coordination compound are shown below.
(a) Give the formula and name for structures 1-3.
(b) Which structures are linkage isomers?
(c) Which structures are ionization isomers?
Look at the location in the periodic table of elements A, B, C, and D. What is the electron configuration of the transition metal in each of the following ions?
(a) A2+
(b) B+