Constitutional isomers of a ruthenium(II) coordination compound are shown below.
(a) Give the formula and name for structures 1-3.
(b) Which structures are linkage isomers?
(c) Which structures are ionization isomers?

 McMurry 8th Edition
McMurry 8th Edition Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry
Ch.21 - Transition Elements and Coordination Chemistry Problem 21.87b
Problem 21.87b Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceDiastereoisomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror images of each other. In coordination complexes, they arise when there are multiple chiral centers or when the ligands can be arranged in different spatial configurations.
This complex has a coordination number of 6, typically forming an octahedral geometry. The ligands are four water molecules and two chloride ions. Consider the possible arrangements of these ligands around the central copper ion.
In an octahedral complex with two identical ligands (Cl-), the ligands can be arranged in either a cis or trans configuration. The cis configuration has the two chloride ions adjacent to each other, while the trans configuration has them opposite each other.
This complex also has a coordination number of 6, suggesting an octahedral geometry. The ligands are three ammonia molecules and three iodide ions. Consider the possible spatial arrangements of these ligands.
With three identical ligands (NH3) and three identical ligands (I-), the complex can form facial (fac) and meridional (mer) isomers. In the fac isomer, the three identical ligands are adjacent, forming a face of the octahedron. In the mer isomer, the three identical ligands form a meridian, spanning the octahedron.

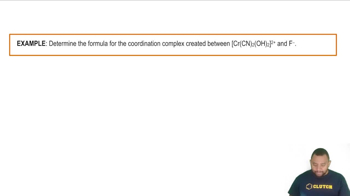
Constitutional isomers of a ruthenium(II) coordination compound are shown below.
(a) Give the formula and name for structures 1-3.
(b) Which structures are linkage isomers?
(c) Which structures are ionization isomers?
Look at the location in the periodic table of elements A, B, C, and D. What is the electron configuration of the transition metal in each of the following ions?
(a) A2+
(b) B+
Give a valence bond description of the bonding in each of the following complexes. Include orbital diagrams for the free metal ion and the metal ion in the complex. Indicate which hybrid orbitals the metal ion uses for bonding, and specify the number of unpaired electrons.
(b) [NiBr4]2- (tetrahedral)
Assign a systematic name to each of the following ions.
(c) [Fe(H2O)5NCS]2+
(d) [Cr(NH3)2(C2O4)2]-
Predict the number of unpaired electrons for each of the following.
(c) Mn3+
(d) Cr2+
Cobalt(III) trifluoroacetylacetonate, Co(tfac)3, is a sixcoordinate, octahedral metal chelate in which three planar, bidentate tfac ligands are attached to a central Co atom:
(b) Diastereoisomers A and B have dipole moments of 6.5 D and 3.8 D, respectively. Which of your diastereoisomers is A and which is B?