Textbook Question
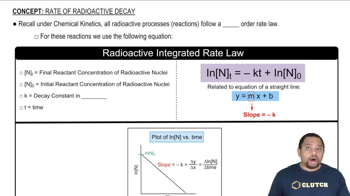
Potassium ion, K+, is present in most foods and is an essen-tial nutrient in the human body. Potassium-40, however, which has a natural abundance of 0.0117%, is radioactive with t1/2 = 1.25 x 10^9 years. What is the decay constant of 40K? How many 40K+ ions are present in 1.00 g of KCl? How many disintegration/s does 1.00 g of KCl undergo?