Nuclear Reactions
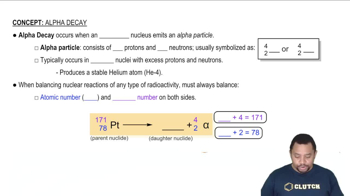
Nuclear reactions involve changes in an atom's nucleus and can result in the formation of new elements. In the context of the question, a nuclear reaction occurs when calcium ions collide with californium, leading to the synthesis of a superheavy element. Understanding how to balance nuclear equations is crucial, as it ensures that the number of protons and neutrons is conserved during the reaction.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance