Textbook Question
On the same graph, sketch pH titration curves for the titra-tion of (1) a strong acid with a strong base and (2) a weak acid with a strong base. How do the two curves differ with respect to the following? (a) The initial pH

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
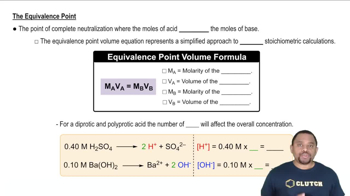

What is the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of 0.10 M solutions of the following acids and bases, and which of the indicators in Figure 17.5 would be suitable for each titration? (a) HNO2 and NaOH
What is the pH at the equivalence point for the titration of 0.10 M solutions of the following acids and bases, and which of the indicators in Figure 17.5 would be suitable for each titration? (c) CH3NH2 (methylamine) and HCl