Textbook Question
Calculate the pH of the following solutions: (c) 0.075 M NaOH

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

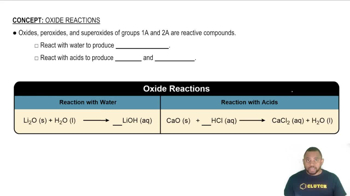
Calculate the pH of solutions prepared by: (a) Dissolving 4.8 g of lithium hydroxide in water to give 250 mL of solution.
Calculate the pH of solutions prepared by: (d) Mixing 100.0 mL of 2.0 * 10-3 M HCl and 400.0 mL of 1.0 * 10-3 M HClO4. (Assume that volumes are additive.)
Look up the values of Ka in Appendix C for C6H5OH, HNO3, CH3CO2H, and HOCl, and arrange these acids in order of: (b) Decreasing percent dissociation.