Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (b) Write a balanced equation for the formation of Cl2O71l2 from the elements.
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 7, Problem 64b
An element X reacts with oxygen to form XO2 and with chlorine to form XCl4. XO2 is a white solid that melts at high temperatures (above 1000 °C). Under usual conditions, XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 58 °C. (b) Do you think that element X is a metal, nonmetal, or metalloid?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the properties of the compounds formed by element X: XO2 is a white solid with a high melting point, and XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a low boiling point.
Analyze the oxidation states and types of compounds formed: XO2 suggests that X forms a dioxide, typical for nonmetals forming covalent bonds with oxygen. XCl4 indicates that X can achieve a +4 oxidation state, common in covalent compounds with nonmetals.
Consider the physical properties of the compounds: The high melting point of XO2 suggests strong covalent bonding typical in nonmetal oxides. The low boiling point of XCl4 suggests volatile nature typical of molecular compounds formed by nonmetals.
Compare with known elements: Elements that form dioxides and tetrachlorides with similar properties are generally nonmetals, such as sulfur forming SO2 and SiCl4.
Conclude the type of element X based on the evidence: Given the covalent nature of the compounds and their physical properties, element X is likely a nonmetal.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Oxidation States and Reactivity
The oxidation state of an element indicates its degree of oxidation or reduction in a compound. In this case, element X forms XO2, suggesting it has a +4 oxidation state when reacting with oxygen, which is typical for nonmetals. Understanding oxidation states helps in predicting the behavior of elements in reactions, particularly in determining whether they are metals, nonmetals, or metalloids.
Recommended video:
Guided course
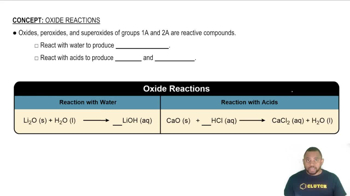
Oxide Reactions
Properties of Compounds
The physical properties of the compounds formed by element X provide insight into its classification. XO2 is a high-melting white solid, characteristic of many nonmetal oxides, while XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a low boiling point, indicating a covalent nature. Analyzing these properties helps in deducing the elemental nature of X based on the behavior of its compounds.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Chemical Properties
Metallic vs. Nonmetallic Characteristics
Metals typically exhibit high melting and boiling points, good conductivity, and form ionic compounds, while nonmetals have lower melting points, can form covalent compounds, and are often insulators. The contrasting properties of XO2 and XCl4 suggest that element X is likely a nonmetal, as it forms a solid oxide with high melting point and a low-boiling liquid chloride.
Recommended video:
Guided course
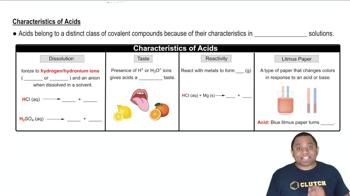
Acid Characteristics
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Chlorine reacts with oxygen to form Cl2O7. (c) Would you expect Cl2O7 to be more reactive toward H+1aq2 or OH-1aq2?
Textbook Question
An element X reacts with oxygen to form XO2 and with chlorine to form XCl4. XO2 is a white solid that melts at high temperatures (above 1000 °C). Under usual conditions, XCl4 is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 58 °C. (a) XCl4 reacts with water to form XO2 and another product. What is the likely identity of the other product?
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the following reactions. a. barium oxide with water
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the following reactions. c. sulfur trioxide with water
Textbook Question
Write balanced equations for the following reactions. d. selenium dioxide with aqueous potassium hydroxide.
