Three solutions are mixed together to form a single solution; in the final solution, there are 0.2 mol Pb1CH3COO)2, 0.1 mol Na2S, and 0.1 mol CaCl2 present. What solid(s) will precipitate?
Ch.4 - Reactions in Aqueous Solution

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 4, Problem 33a
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (a) Sulfuric acid is a monoprotic acid.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Sulfuric acid (H_2SO_4) is a strong acid commonly used in various chemical processes.
The term 'monoprotic' refers to an acid that can donate only one proton (H^+) per molecule in an aqueous solution.
To determine if sulfuric acid is monoprotic, consider its chemical formula, H_2SO_4, which indicates it has two hydrogen atoms that can potentially be donated as protons.
In aqueous solution, sulfuric acid dissociates in two steps: the first step involves the donation of one proton, forming the bisulfate ion (HSO_4^-), and the second step involves the donation of a second proton, forming the sulfate ion (SO_4^{2-}).
Since sulfuric acid can donate two protons, it is classified as a diprotic acid, not a monoprotic acid. Therefore, the statement is false.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Monoprotic Acids
Monoprotic acids are acids that can donate only one proton (H⁺ ion) per molecule during the process of dissociation in an aqueous solution. This characteristic is crucial for understanding the acid's strength and behavior in chemical reactions. Examples of monoprotic acids include hydrochloric acid (HCl) and acetic acid (CH₃COOH).
Recommended video:
Guided course

Binary Acids
Sulfuric Acid
Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄) is a strong diprotic acid, meaning it can donate two protons per molecule. The first dissociation releases one proton, while the second dissociation releases another proton, making it capable of acting as both a monoprotic and diprotic acid depending on the context. This property is essential for understanding its reactivity and applications in various chemical processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course
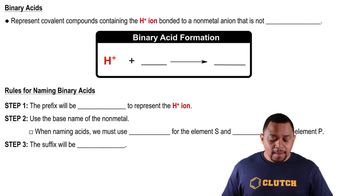
Binary Acids
Acid Strength and Classification
Acid strength refers to the ability of an acid to donate protons in solution, which is influenced by its molecular structure and the stability of its conjugate base. Acids are classified as strong or weak based on their degree of ionization in water. Understanding this classification helps in predicting the behavior of acids in chemical reactions and their interactions with bases.
Recommended video:
Guided course
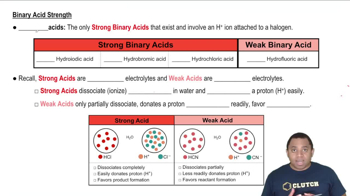
Binary Acid Strengths
Related Practice
Textbook Question
2
views
Textbook Question
Which of the following solutions is the most acidic? a. 0.2 M LiOH b. 0.2 M HI c. 1.0 M methanol (CH3OH)
Textbook Question
Which of the following solutions is the most basic? a. 0.6𝑀 NH3 b. 0.150 M KOH c. 0.100𝑀Ba(OH)2
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (b) HCl is a weak acid.
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (c) Methanol is a base.
Textbook Question
State whether each of the following statements is true or false. Justify your answer in each case. (a) NH3 contains no OH- ions, and yet its aqueous solutions are basic
