Predict the type of radioactive decay process for the following radionuclides: (c) phosphorus-32. (d) chlorine-39.

One of the nuclides in each of the following pairs is radioactive. Predict which is radioactive and which is stable: (a) 39₁₉K and 40₁₉K. (b) ²⁰⁹Bi and ²⁰⁸Bi. (c) nickel-58 and nickel-65.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Radioactive Decay
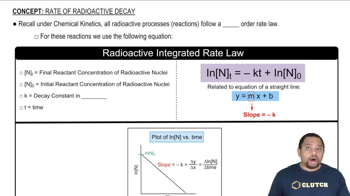
Nuclide Stability
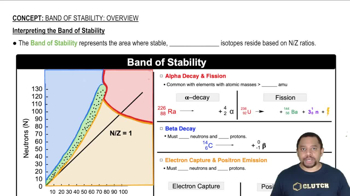
Isotopes

Each of the following nuclei undergoes either beta decay or positron emission. Predict the type of emission for each: (a) tritium, 31H.
Each of the following nuclei undergoes either beta decay or positron emission. Predict the type of emission for each: b. 9938Sr
Despite the similarities in the chemical reactivity of elements in the lanthanide series, their abundances in Earth's crust vary by two orders of magnitude. This graph shows the relative abundance as a function of atomic number. Which of the following statements best explains the sawtooth variation across the series? (a) The elements with an odd atomic number lie above the belt of stability. (b) The elements with an odd atomic number lie below the belt of stability. (c) The elements with an even atomic number have a magic number of protons. (d) Pairs of protons have a special stability.
