Textbook Question
Predict the type of radioactive decay process for the following radionuclides: (c) phosphorus-32. (d) chlorine-39.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
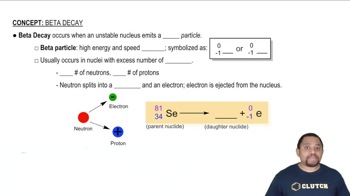
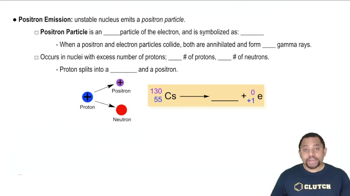
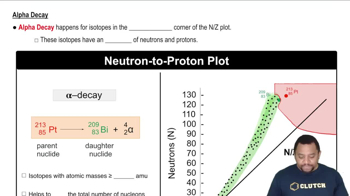
Predict the type of radioactive decay process for the following radionuclides: (c) phosphorus-32. (d) chlorine-39.
Predict the type of radioactive decay process for the following radionuclides: (b) 6829Cu.
Each of the following nuclei undergoes either beta decay or positron emission. Predict the type of emission for each: (a) tritium, 31H.