A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: 2 Fe3+1aq2 + H21g2 ¡ 2 Fe2+1aq2 + 2 H+1aq2 (a) What is the emf of this cell under standard conditions?
Ch.20 - Electrochemistry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 20, Problem 76a
A voltaic cell is constructed that is based on the following reaction: Sn2+(aq) + Pb(s) → Sn(s) + Pb2+(aq) (a) If the concentration of Sn2+ in the cathode half-cell is 1.00 M and the cell generates an emf of +0.22 V, what is the concentration of Pb2+ in the anode half-cell?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the half-reactions at the cathode and anode. For the cathode, the reduction reaction is Sn2+ + 2e- → Sn(s). For the anode, the oxidation reaction is Pb(s) → Pb2+ + 2e-.
Write the overall cell reaction by combining the half-reactions: Sn2+ + Pb(s) → Sn(s) + Pb2+.
Use the Nernst equation to relate the cell potential to the concentrations of the reactants and products. The Nernst equation is E = E^0 - (RT/nF) * ln(Q), where E is the cell potential, E^0 is the standard cell potential, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, n is the number of moles of electrons transferred, F is the Faraday constant, and Q is the reaction quotient.
Calculate the reaction quotient, Q, for the reaction at the given conditions. Since the concentration of Sn2+ is given as 1.00 M, and assuming standard conditions for the other species (1 M for Pb2+ initially), Q can be calculated as Q = [Pb2+]/[Sn2+].
Substitute the known values and solve the Nernst equation for the concentration of Pb2+ in the anode half-cell. Rearrange the equation to isolate [Pb2+] and solve for its concentration using the given emf of +0.22 V.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
9mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical cells, including voltaic cells, convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. In a voltaic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode, allowing for the flow of electrons through an external circuit. Understanding the roles of the anode and cathode is essential for analyzing the cell's behavior and calculating cell potential.
Recommended video:
Guided course
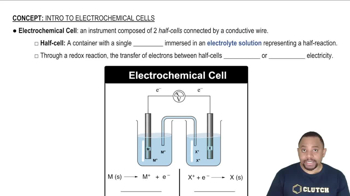
Electrochemical Cells
Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation relates the cell potential to the concentrations of the reactants and products in a redox reaction. It allows for the calculation of the electromotive force (emf) under non-standard conditions, taking into account the temperature and concentration of ions. This equation is crucial for determining the concentration of Pb2+ in the anode half-cell based on the given emf and concentration of Sn2+.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Nernst Equation
Standard Electrode Potentials
Standard electrode potentials are measured values that indicate the tendency of a species to be reduced, measured under standard conditions. Each half-reaction has a specific standard potential, which can be used to predict the direction of electron flow in a cell. Knowing the standard potentials for the Sn2+/Sn and Pb2+/Pb half-reactions is necessary to calculate the overall cell potential and apply the Nernst equation effectively.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Standard Cell Potential
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: (b) What is the emf for this cell when 3Fe3+4 = 3.50 M, PH2= 0.95 atm, 3Fe2+4 = 0.0010 M, and the pH in both half-cells is 4.00?
1
views
Textbook Question
During a period of discharge of a lead–acid battery, 402 g of Pb from the anode is converted into PbSO4(s). (a) What mass of PbO2(s) is reduced at the cathode during this same period?
Textbook Question
During a period of discharge of a lead–acid battery, 402 g of Pb from the anode is converted into PbSO4(s). (b) How many coulombs of electrical charge are transferred from Pb to PbO2?
Textbook Question
During the discharge of an alkaline battery, 4.50 g of Zn is consumed at the anode of the battery. (b) How many coulombs of electrical charge are transferred from Zn to MnO2?
