A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: 4 Fe2+1aq2 + O21g2 + 4 H+1aq2 ¡ 4 Fe3+1aq2 + 2 H2O1l2 (a) What is the emf of this cell under standard conditions?
Ch.20 - Electrochemistry

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 20, Problem 72a
A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: 2 Fe3+1aq2 + H21g2 ¡ 2 Fe2+1aq2 + 2 H+1aq2 (a) What is the emf of this cell under standard conditions?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Step 1: Identify the half-reactions involved in the overall cell reaction.
Step 2: Write the reduction half-reaction and the oxidation half-reaction separately.
Step 3: Use the standard reduction potentials from a table to find the potential for each half-reaction.
Step 4: Calculate the standard cell potential (emf) by subtracting the oxidation potential from the reduction potential.
Step 5: Ensure the units are consistent and the final expression is in volts (V).

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
4mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electrochemical Cells
Electrochemical cells are devices that convert chemical energy into electrical energy through redox reactions. A voltaic cell, specifically, generates electricity spontaneously from a chemical reaction, involving oxidation and reduction processes occurring in separate half-cells. Understanding the structure and function of these cells is essential for analyzing their emf (electromotive force) and overall efficiency.
Recommended video:
Guided course
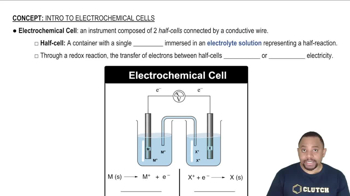
Electrochemical Cells
Standard Electrode Potentials
Standard electrode potentials are measured voltages that indicate the tendency of a species to be reduced, measured under standard conditions (1 M concentration, 1 atm pressure, and 25°C). Each half-reaction in a voltaic cell has a specific standard electrode potential, which can be used to calculate the overall cell potential (emf) by subtracting the anode potential from the cathode potential. This concept is crucial for determining the emf of the cell in the given reaction.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Standard Cell Potential
Nernst Equation
The Nernst equation relates the emf of an electrochemical cell to the concentrations of the reactants and products involved in the redox reaction. It allows for the calculation of the cell potential under non-standard conditions, taking into account temperature and concentration variations. Understanding this equation is important for predicting how the emf changes as the reaction progresses or as conditions vary.
Recommended video:
Guided course

The Nernst Equation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: 4 Fe2+1aq2 + O21g2 + 4 H+1aq2 ¡ 4 Fe3+1aq2 + 2 H2O1l2 (b) What is the emf of this cell when 3Fe2+4 = 1.3 M, 3Fe3+4= 0.010 M, PO2 = 0.50 atm, and the pH of the solution in the cathode half-cell is 3.50?
Textbook Question
A voltaic cell utilizes the following reaction: (b) What is the emf for this cell when 3Fe3+4 = 3.50 M, PH2= 0.95 atm, 3Fe2+4 = 0.0010 M, and the pH in both half-cells is 4.00?
1
views
Textbook Question
A voltaic cell is constructed that is based on the following reaction: Sn2+(aq) + Pb(s) → Sn(s) + Pb2+(aq) (a) If the concentration of Sn2+ in the cathode half-cell is 1.00 M and the cell generates an emf of +0.22 V, what is the concentration of Pb2+ in the anode half-cell?
