The capacity of batteries such as the typical AA alkaline battery is expressed in units of milliamp-hours (mAh). An AA alkaline battery yields a nominal capacity of 2850 mAh. (b) The starting voltage of a fresh alkaline battery is 1.55 V. The voltage decreases during discharge and is 0.80 V when the battery has delivered its rated capacity. If we assume that the voltage declines linearly as current is withdrawn, estimate the total maximum electrical work the battery could perform during discharge.

(a) How many coulombs are required to plate a layer of chromium metal 0.25 mm thick on an auto bumper with a total area of 0.32 m² from a solution containing CrO₄²⁻? The density of chromium metal is 7.20 g/cm³. (b) What current flow is required for this electroplating if the bumper is to be plated in 10.0 s? (c) If the external source has an emf of +6.0 V and the electrolytic cell is 65% efficient, how much electrical power is expended to electroplate the bumper?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Electroplating and Faraday's Laws

Current and Time Relationship
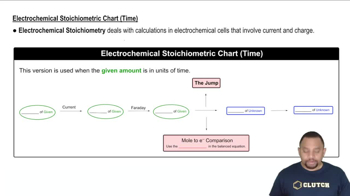
Efficiency and Power in Electrolytic Cells

Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (b) What is the oxidation state of sulfur in a disulfide?
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (c) If you react two thiols to make a disulfide, are you oxidizing or reducing the thiols?
Calculate the number of kilowatt-hours of electricity required to produce 1.0 * 103 kg (1 metric ton) of aluminum by electrolysis of Al3+ if the applied voltage is 4.50 V and the process is 45% efficient.
Aqueous solutions of ammonia (NH3) and bleach (active ingredient NaOCl) are sold as cleaning fluids, but bottles of both of them warn: 'Never mix ammonia and bleach, as toxic gases may be produced.' One of the toxic gases that can be produced is chloroamine, NH2Cl. (a) What is the oxidation number of chlorine in bleach? (active ingredient NaOCl) are sold as cleaning fluids, but bottles of both of them warn: “Never mix ammonia and bleach, as toxic gases may be produced.” One of the toxic gases that can be produced is chloroamine, NH2Cl. (b) What is the oxidation number of chlorine in chloramine? (d) Another toxic gas that can be produced is nitrogen trichloride, NCl3. What is the oxidation number of N in nitrogen trichloride?
Aqueous solutions of ammonia 1NH32 and bleach (active ingredient NaOCl) are sold as cleaning fluids, but bottles of both of them warn: 'Never mix ammonia and bleach, as toxic gases may be produced.' One of the toxic gases that can be produced is chloroamine, NH2Cl. (e) Is N oxidized, reduced, or neither, upon the conversion of ammonia to nitrogen trichloride?
