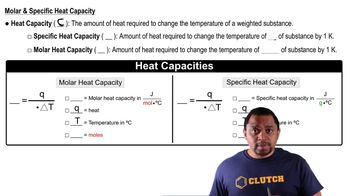
A voltaic cell is constructed that uses the following half-cell reactions:
Cu+(aq) + e- → Cu(s)
I2(s) + 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)
The cell is operated at 298 K with [Cu+] = 0.25 M and [I-] = 0.035 M.
(a) Determine E for the cell at these concentrations.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

A voltaic cell is constructed that uses the following half-cell reactions:
Cu+(aq) + e- → Cu(s)
I2(s) + 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)
The cell is operated at 298 K with [Cu+] = 0.25 M and [I-] = 0.035 M.
(a) Determine E for the cell at these concentrations.
A voltaic cell is constructed that uses the following half-cell reactions:
Cu+(aq) + e- → Cu(s)
I2(s) + 2 e- → 2 I-(aq)
The cell is operated at 298 K with [Cu+] = 0.25 M and [I-] = 0.035 M.
(b) Which electrode is the anode of the cell?
(c) Is the answer to part (b) the same as it would be if the cell were operated under standard conditions?
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (b) What is the oxidation state of sulfur in a disulfide?
Disulfides are compounds that have S ¬ S bonds, like peroxides have O ¬ O bonds. Thiols are organic compounds that have the general formula R ¬ SH, where R is a generic hydrocarbon. The SH- ion is the sulfur counterpart of hydroxide, OH-. Two thiols can react to make a disulfide, R ¬ S ¬ S ¬ R. (c) If you react two thiols to make a disulfide, are you oxidizing or reducing the thiols?