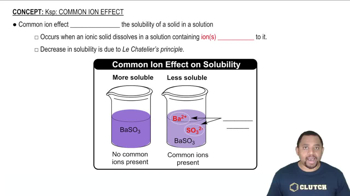
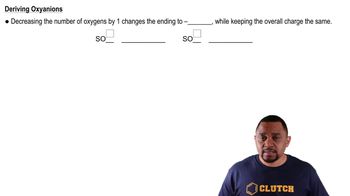
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the third column of the table.
Complete the fourth column of the table.