Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the first column of the table.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the first column of the table.
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the third column of the table.
Complete the fourth column of the table.
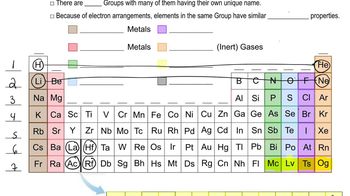
Elements in the same group of the periodic table often form oxyanions with the same general formula. The anions are also named in a similar fashion. Based on these observations, suggest a chemical formula or name, as appropriate, for each of the following ions: (d) hydrogen tellurate ion.
Many familiar substances have common, unsystematic names. For each of the following, give the correct systematic name: (a) salt peter, KNO3 (b) soda ash, Na2CO3 (c) lime, (d) muriatic acid, HCl, CaO (e) Epsom salts, MgSO4 (f) milk of magnesia, Mg(OH)2.