From the following list of elements—Ar, H, Ga, Al, Ca, Br, Ge, K, O—pick the one that best fits each description. Use each element only once: (a) an alkali metal, (b) an alkaline earth metal, (c) a noble gas, (d) a halogen, (e) a metalloid, (f) a nonmetal listed in group 1A, (g) a metal that forms a 3+ ion, (h) a nonmetal that forms a 2- ion, (i) an element that resembles aluminum.

From the molecular structures shown here, identify the one that corresponds to each of the following species: (a) chlorine gas; (b) propane; (c) nitrate ion; (d) sulfur trioxide; (e) methyl chloride, CH3Cl.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
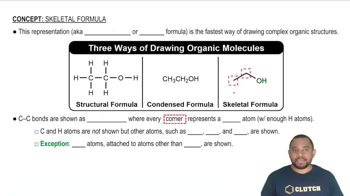
Molecular Structure
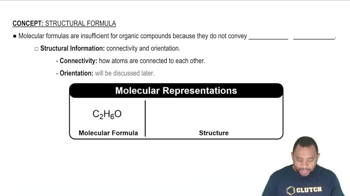
Chemical Formula
Ionic vs. Covalent Compounds

The first atoms of seaborgium (Sg) were identified in 1974. The longest-lived isotope of Sg has a mass number of 266. (a) How many protons, electrons, and neutrons are in an 266Sg atom?
The first atoms of seaborgium (Sg) were identified in 1974. The longest-lived isotope of Sg has a mass number of 266. (b) Atoms of Sg are very unstable, and it is therefore difficult to study this element's properties. Based on the position of Sg in the periodic table, what element should it most closely resemble in its chemical properties?
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the first column of the table.
Fill in the blanks in the following table:
Cation Anion Formula Name
Lithium oxide
Fe2+ PO43-
Al2(SO4)3
Copper(II) nitrate
Cr3+ I−
MnClO2
Ammonium carbonate
Zinc perchlorate
Complete the third column of the table.
Complete the fourth column of the table.
