Which of the following statements is false? (a) An Arrhenius base increases the concentration of OH- in water. (b) A Brønsted-Lowry base is a proton acceptor. (c) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry acid. (d) Water can act as a Brønsted–Lowry base. (e) Any compound that contains an –OH group acts as a Brønsted-Lowry base.

Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HIO3, (ii) NH4+.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
Brønsted–Lowry Acid-Base Theory

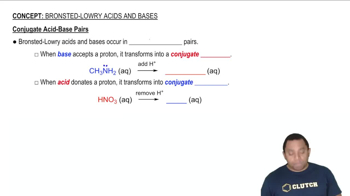
Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs
Dissociation of Acids

Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base among the reactants in each of the following reactions:
(a) Fe(ClO4)3(s) + 6 H2O(l) ⇌ [Fe(H2O)6]3+(aq) + 3 ClO4-(aq)
(b) CN-(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ HCN(aq) + OH-(aq)
(c) (CH3)3N(g) + BF3(g) ⇌ (CH3)NBF3(s)
(d) HIO(lq) + NH2-(lq) ⇌ NH3(lq) + IO-(lq) (lq denotes liquid ammonia as solvent)
Identify the Lewis acid and Lewis base in each of the following reactions:
(a) HNO2(aq) + OH-(aq) ⇌ NO2-(aq) + H2O(l)
(b) FeBr3(s) + Br-(aq) ⇌ FeBr4-(aq)
(c) Zn2+(aq) + 4 NH3(aq) ⇌ Zn(NH3)42+(aq)
(d) SO2(g) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2SO3(aq)
Give the conjugate acid of the following Brønsted–Lowry bases: (i) SO42-, (ii) CH3NH2.
Give the conjugate base of the following Brønsted–Lowry acids: (i) HCOOH, (ii) HPO42-.
Identify the Brønsted–Lowry acid and the Brønsted–Lowry base on the left side of each of the following equations, and also identify the conjugate acid and conjugate base of each on the right side:
(a) NH4+(aq) + CN-(aq) ⇌ HCN(aq) + NH3(aq)
(b) (CH3)3N(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ (CH3)3NH+(aq) + OH-(aq)
(c) HCOOH(aq) + PO43-(aq) ⇌ HCOO-(aq)+ HPO42-(aq)
