The presence of the radioactive gas radon (Rn) in well water presents a possible health hazard in parts of the United States. (a) Assuming that the solubility of radon in water with 1 atm pressure of the gas over the water at 30 °C is 7.27⨉10-3 M, what is the Henry's law constant for radon in water at this temperature?

The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (a) Calculate the molarity of lead in a 9.0-ppb solution.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
Key Concepts
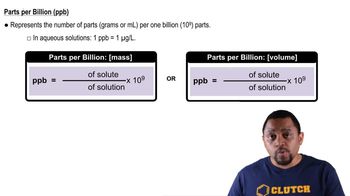
Parts Per Billion (ppb)
Molarity

Molar Mass of Lead

The presence of the radioactive gas radon (Rn) in well water presents a possible health hazard in parts of the United States. (b) A sample consisting of various gases contains 3.5 × 10-6 mole fraction of radon. This gas at a total pressure of 32 atm is shaken with water at 30 °C. Calculate the molar concentration of radon in the water.
The maximum allowable concentration of lead in drinking water is 9.0 ppb. (b) How many grams of lead are in a swimming pool containing 9.0 ppb lead in 60 m3 of water?
The first stage of treatment at a reverse osmosis plant is to flow the water through rock, sand, and gravel as shown here. Would this step remove particulate matter? Would this step remove dissolved salts?
Acetonitrile (CH3CN) is a polar organic solvent that dissolves a wide range of solutes, including many salts. The density of a 1.80 M LiBr solution in acetonitrile is 0.826 g/cm3. Calculate the concentration of the solution in (a) molality,
