What pressure, in atmospheres, is exerted on the body of a diver if they are 15 ft below the surface of the water when the atmospheric pressure is 750 torr? Assume that the density of the water is 1.00 g/cm3=1.00×103 kg/m3. The gravitational constant is 9.81 m/s2, and 1 Pa=1 kg/m-s2.
Ch.10 - Gases

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 10, Problem 19d
The typical atmospheric pressure on top of Mount Everest (29,032 ft) is about 265 torr. Convert this pressure to d. bars,
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand the units involved: 1 bar is equivalent to 1000 millibars (mbar) and 1 bar is approximately equal to 750.06 torr.
Set up the conversion factor from torr to bar. Since 1 bar = 750.06 torr, the conversion factor is 1 bar / 750.06 torr.
Multiply the given pressure in torr (265 torr) by the conversion factor to convert it to bars: (265 torr) * (1 bar / 750.06 torr).
Simplify the expression by canceling out the torr units, leaving you with the pressure in bars.
Perform the division to find the pressure in bars, ensuring to keep track of significant figures based on the given data.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Pressure Units
Pressure is a measure of the force exerted per unit area. Common units for pressure include torr, pascal, and bar. Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for solving problems related to atmospheric pressure, as different contexts may require different units.
Recommended video:
Guided course
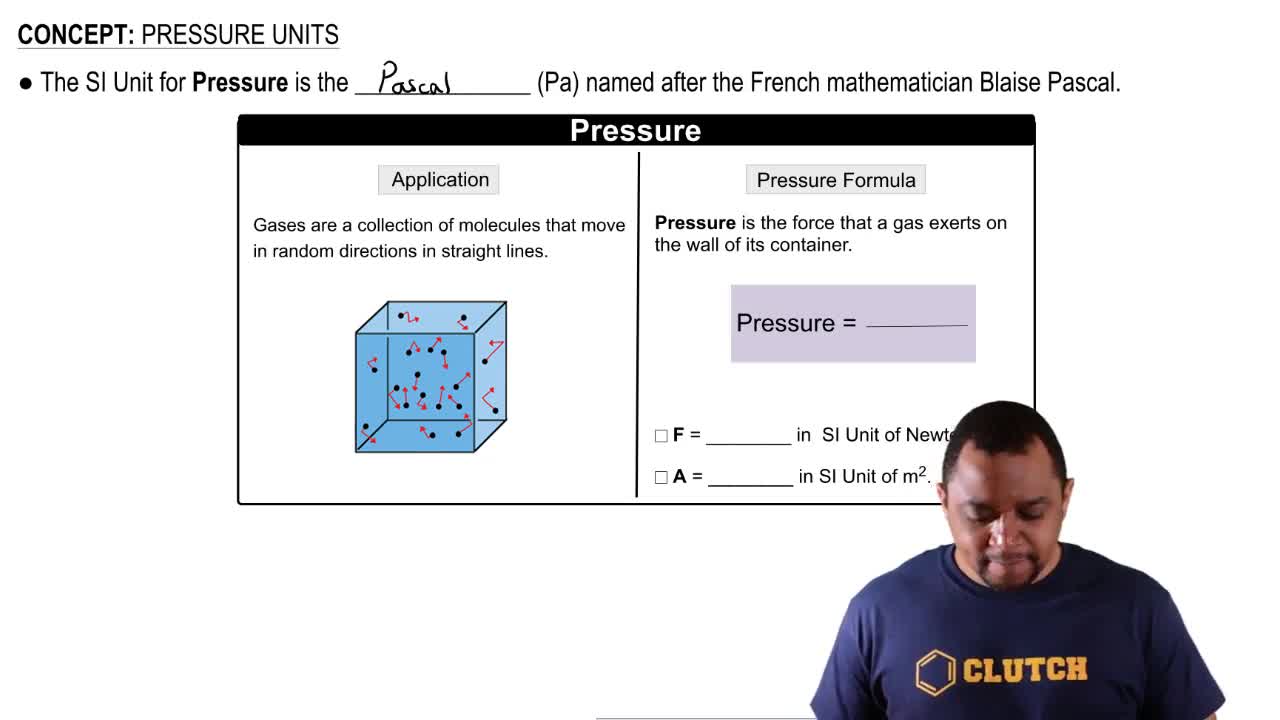
Pressure Units
Conversion Factors
Conversion factors are ratios used to convert a quantity from one unit to another. For pressure, knowing the relationship between torr and d. bars is crucial. Specifically, 1 d. bar is equivalent to 1000 millibar, and 1 torr is approximately 1.33322 millibar, which allows for accurate conversions between these units.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Conversion Factors
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the pressure exerted by the weight of the atmosphere above a given point. It varies with altitude; for example, at higher elevations like Mount Everest, the atmospheric pressure is significantly lower than at sea level. Understanding this concept helps contextualize the pressure values being converted.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Total Pressure Example
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
(a) The compound 1-iodododecane is a nonvolatile liquid with a density of 1.20 g>mL. The density of mercury is 13.6 g>mL. What do you predict for the height of a barometer column based on 1-iodododecane, when the atmospheric pressure is 749 torr?
1
views
Textbook Question
The typical atmospheric pressure on top of Mount Everest (29,032 ft) is about 265 torr. Convert this pressure to c. pascals,
Textbook Question
The typical atmospheric pressure on top of Mount Everest (29,032 ft) is about 265 torr. Convert this pressure to e. psi.
Textbook Question
Perform the following conversions: (b) 0.685 bar to kilopascals
Textbook Question
Perform the following conversions: (d) 1.323 * 105 Pa to atmospheres
