A watt is a measure of power (the rate of energy change) equal to 1 J/s. (b) An adult person radiates heat to the surroundings at about the same rate as a 100-watt electric incandescent light bulb. What is the total amount of energy in kcal radiated to the surroundings by an adult over a 24 h period?
Ch.1 - Introduction: Matter, Energy, and Measurement

Brown15th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780137542970Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 1, Problem 85a
Two spheres of equal volume are placed on the scales as shown. a. Which one is more dense?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
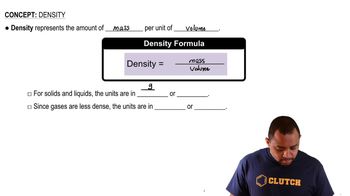
Identify the concept of density: Density is defined as mass per unit volume, expressed as \( \rho = \frac{m}{V} \).
Recognize that both spheres have equal volume, meaning \( V_1 = V_2 \).
Understand that the density of each sphere depends on its mass, since the volumes are equal.
Observe the scales: The sphere that causes the scale to tip more is the one with greater mass.
Conclude that the sphere with greater mass is more dense, as density is directly proportional to mass when volume is constant.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Density
Density is defined as mass per unit volume, typically expressed in grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³). It is a physical property that indicates how much matter is packed into a given space. In this scenario, comparing the density of the two spheres involves determining which one has a greater mass while maintaining the same volume.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Density Concepts
Mass
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, usually measured in grams or kilograms. It is an intrinsic property that does not change regardless of the object's location. In the context of the question, the mass of each sphere is crucial for determining their respective densities, as density is calculated by dividing mass by volume.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Atomic Mass
Volume
Volume is the amount of space an object occupies, typically measured in cubic centimeters (cm³) or liters. For the two spheres mentioned, since they are stated to have equal volume, this factor remains constant when comparing their densities. Understanding volume is essential for calculating density, as it serves as the denominator in the density formula.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Constant-Volume Calorimetry
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Water has a density of 0.997 g/cm3 at 25 °C; ice has a density of 0.917 g/cm3 at -10 °C. (a) If a soft-drink bottle whose volume is 1.50 L is completely filled with water and then frozen to -10 °C, what volume does the ice occupy? (b) Can the ice be contained within the bottle?
Textbook Question
A 32.65-g sample of a solid is placed in a flask. Toluene, in which the solid is insoluble, is added to the flask so that the total volume of solid and liquid together is 50.00 mL. The solid and toluene together weigh 58.58 g. The density of toluene at the temperature of the experiment is 0.864 g/mL. What is the density of the solid?
4
views
