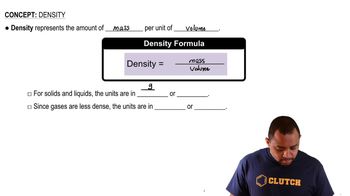
Textbook Question
A watt is a measure of power (the rate of energy change) equal to 1 J/s. (b) An adult person radiates heat to the surroundings at about the same rate as a 100-watt electric incandescent light bulb. What is the total amount of energy in kcal radiated to the surroundings by an adult over a 24 h period?
1
views