Textbook Question
Consider the SCl2 molecule. (c) What hybrid orbitals should be constructed on the S atom to make the S-Cl bonds in SCl2?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance

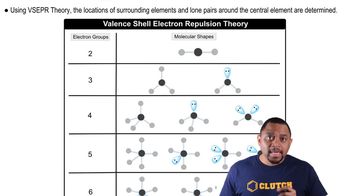
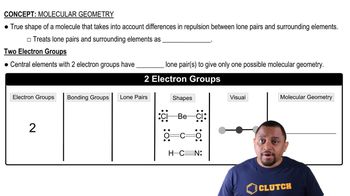
Consider the SCl2 molecule. (c) What hybrid orbitals should be constructed on the S atom to make the S-Cl bonds in SCl2?
Consider the SCl2 molecule.(d) What valence orbitals, if any, remain unhybridized on the S atom in SCl2?
Indicate the hybridization of the central atom in (a) H2S (b) SeF6
What is the hybridization of the central atom in (a) PBr5? (b) CH2O?
What is the hybridization of the central atom in (c) O3?
What is the hybridization of the central atom in (d) NO2?