Textbook Question
(a) Draw a picture showing how two p orbitals on two different atoms can be combined to make a σ bond. (b) Sketch a π bond that is constructed from p orbitals.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
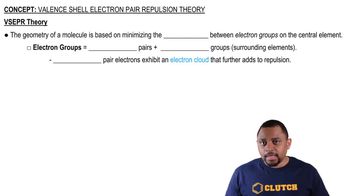
(a) Draw a picture showing how two p orbitals on two different atoms can be combined to make a σ bond. (b) Sketch a π bond that is constructed from p orbitals.
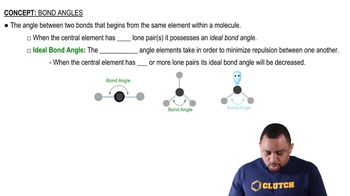
(c) Which is generally stronger, a s bond or a p bond? Explain.
(d) Can two s orbitals combine to form a p bond? Explain.
(b) Imagine that you could hold two atoms that are bonded together, twist them, and not change the bond length. Would it be easier to twist (rotate) around a single s bond or around a double 1s plus p2 bond, or would they be the same?
(a) Draw Lewis structures for chloromethane (CH3Cl), chloroethene (C2H3Cl), and chloroethyne (C2HCl).
(b) What is the hybridization of the carbon atoms in each molecule?