In the following pairs of binary compounds, determine which one is a molecular substance and which one is an ionic substance. Use the appropriate naming convention (for ionic or molecular substances) to assign a name to each compound: (a) TiCl4 and CaF2 (b) ClF3 and VF3
Ch.8 - Basic Concepts of Chemical Bonding

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 8, Problem 43b
(b) If you were to put HBr under very high pressure, so its bond length decreased significantly, would its dipole moment increase, decrease, or stay the same, if you assume that the effective charges on the atoms do not change?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that the dipole moment (\(\mu\)) is calculated using the formula \(\mu = q \times d\), where \(q\) is the charge and \(d\) is the bond length.
Recognize that the problem states the effective charges on the atoms do not change, meaning \(q\) remains constant.
Note that the bond length \(d\) is decreasing due to high pressure.
Since \(\mu = q \times d\) and \(q\) is constant, a decrease in \(d\) will lead to a decrease in the dipole moment \(\mu\).
Conclude that the dipole moment of HBr will decrease if the bond length decreases significantly under high pressure.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Dipole Moment
The dipole moment is a measure of the separation of positive and negative charges in a molecule, indicating the polarity of the bond. It is calculated as the product of the charge and the distance between the charges. A higher dipole moment signifies a more polar bond, while a dipole moment of zero indicates a nonpolar bond.
Recommended video:
Guided course
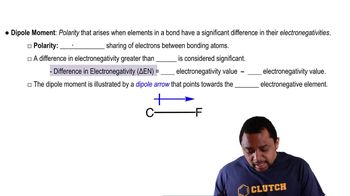
Dipole Moment
Bond Length and Polarity
Bond length refers to the distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms. In general, as bond length decreases, the electron density between the atoms increases, which can enhance the bond's polarity. However, if the effective charges remain unchanged, the overall dipole moment may not necessarily increase, despite the shorter bond length.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Molecular Polarity
Effect of Pressure on Molecular Structure
Applying high pressure to a gas can lead to a decrease in bond lengths due to the closer proximity of atoms. This compression can alter molecular interactions and properties, but if the effective charges on the atoms do not change, the intrinsic polarity of the bond, and thus the dipole moment, may remain constant despite the change in bond length.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Photoelectric Effect
Related Practice
Textbook Question
1
views
Textbook Question
Arrange the bonds in each of the following sets in order of increasing polarity: (a) C—F, O—F, Be—F (b) O—Cl,S—Br, C—P
Textbook Question
Arrange the bonds in each of the following sets in order of increasing polarity: (c) C—S, B—F, N—O.
Textbook Question
(a) From the data in Table 8.2, calculate the effective charges on the H atom of the HBr molecule in units of the electronic charge, e.
4
views
Textbook Question
The iodine monobromide molecule, IBr, has a bond lengthof 249 pm and a dipole moment of 1.21 D. (a) Which atom ofthe molecule is expected to have a negative charge?
Textbook Question
In the following pairs of binary compounds, determine which one is a molecular substance and which one is an ionic substance. Use the appropriate naming convention (for ionic or molecular substances) to assign a name to each compound: (a) SiF4 and LaF3 (for ionic or molecular substances) to assign a name to each compound: (b) FeCl2 and ReCl6 (c) PbCl4 and RbCl.
1
views
