Elements in group 7A in the periodic table are called the halogens; elements in group 6A are called the chalcogens. (a) What is the most common oxidation state of the chalcogens compared to the halogens?
Ch.7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 7, Problem 89
(a) Which ion is smaller, Co3+ or Co4+? (b) In a lithium-ion battery that is discharging to power a device, for every Li+ that inserts into the lithium cobalt oxide electrode, a Co4+ ion must be reduced to a Co3+ ion to balance charge. Using the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics or other standard reference, find the ionic radii of Li+, Co3+, and Co4+. Order these ions from smallest to largest.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
To determine which ion is smaller between Co3+ and Co4+, consider the concept of effective nuclear charge. As the positive charge on the ion increases, the effective nuclear charge experienced by the electrons also increases, pulling them closer to the nucleus and resulting in a smaller ionic radius. Therefore, Co4+ is expected to be smaller than Co3+.
In a lithium-ion battery, when a Li+ ion inserts into the lithium cobalt oxide electrode, a Co4+ ion is reduced to Co3+. This process maintains charge balance within the electrode.
To find the ionic radii of Li+, Co3+, and Co4+, consult a reliable reference such as the CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. Look up the specific ionic radii values for each ion.
Once you have the ionic radii values, compare them to order the ions from smallest to largest. Remember that the ionic radius is influenced by the charge and the number of electrons in the ion.
Based on the typical trends and the data from the reference, you should be able to order the ions. Generally, Co4+ will be the smallest due to its higher positive charge, followed by Co3+, and then Li+ as the largest due to its lower charge and larger ionic radius.
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Ionic Radius
The ionic radius is a measure of the size of an ion in a crystal lattice. It is influenced by the ion's charge and the number of electrons relative to protons. Cations, which are positively charged ions, are generally smaller than their neutral atoms due to the loss of electrons and increased effective nuclear charge, which pulls the remaining electrons closer to the nucleus.
Recommended video:
Guided course
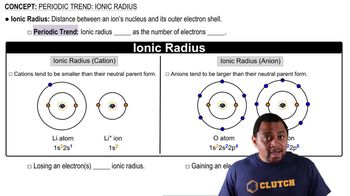
Ionic Radius
Oxidation States
Oxidation states indicate the degree of oxidation of an atom in a compound, reflecting the number of electrons lost or gained. In the case of cobalt, Co3+ has lost three electrons, while Co4+ has lost four. The higher the oxidation state, the greater the positive charge, which typically results in a smaller ionic radius due to increased attraction between the nucleus and the remaining electrons.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Oxidation Numbers
Lithium-Ion Battery Chemistry
In lithium-ion batteries, lithium ions (Li+) move between the anode and cathode during charging and discharging. The reduction of Co4+ to Co3+ in the cathode during discharge is crucial for maintaining charge balance. Understanding this process is essential for analyzing the performance and efficiency of lithium-ion batteries, as it directly relates to the movement of ions and the associated changes in oxidation states.
Recommended video:
Guided course
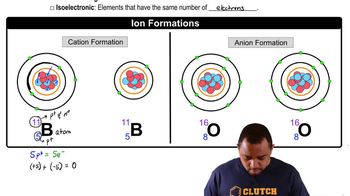
Ion Formation
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Note from the following table that there is a significant increasein atomic radius upon moving from Y to La, whereasthe radii of Zr to Hf are the same. Suggest an explanation forthis effect.Atomic Radii (pm)Sc 170 Ti 160Y 190 Zr 175La 207 Hf 175
Textbook Question
(c) Will the lithium cobalt oxide cathode expand or contract as lithium ions are inserted?
Textbook Question
(d) Lithium is not nearly as abundant as sodium. If sodium ion batteries were developed that function in the same manner as lithium ion batteries, do you think 'sodium cobalt oxide' would still work as the electrode material? Explain.
1
views
Textbook Question
The ionic substance strontium oxide, SrO, forms from the reaction of strontium metal with molecular oxygen. The arrangement of the ions in solid SrO is analogous to that in solid NaCl: (a) Write a balanced equation for the formation of SrO(s) from its elements.
