The Lyman series of emission lines of the hydrogen atom are those for which nf = 1. (b) Calculate the wavelengths of the first three lines in the Lyman series—those for which ni = 2, 3, and 4.
Ch.6 - Electronic Structure of Atoms

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 6, Problem 44a
The hydrogen atom can absorb light of wavelength 1094 nm. (a) In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this absorption found?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the given wavelength of light absorbed by the hydrogen atom, which is 1094 nm.
Convert the wavelength from nanometers to meters for standard unit consistency. Use the conversion factor: 1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m.
Recall the regions of the electromagnetic spectrum and their corresponding wavelength ranges. The main regions include radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays.
Determine which region the wavelength of 1094 nm falls into by comparing it to the known wavelength ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. For example, the infrared region typically ranges from about 700 nm to 1 mm.
Conclude that the absorption of light by the hydrogen atom at 1094 nm falls within the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses all types of electromagnetic radiation, arranged by wavelength or frequency. It includes various regions such as radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays. Understanding where a specific wavelength falls within this spectrum is crucial for identifying its properties and interactions with matter.
Recommended video:
Guided course
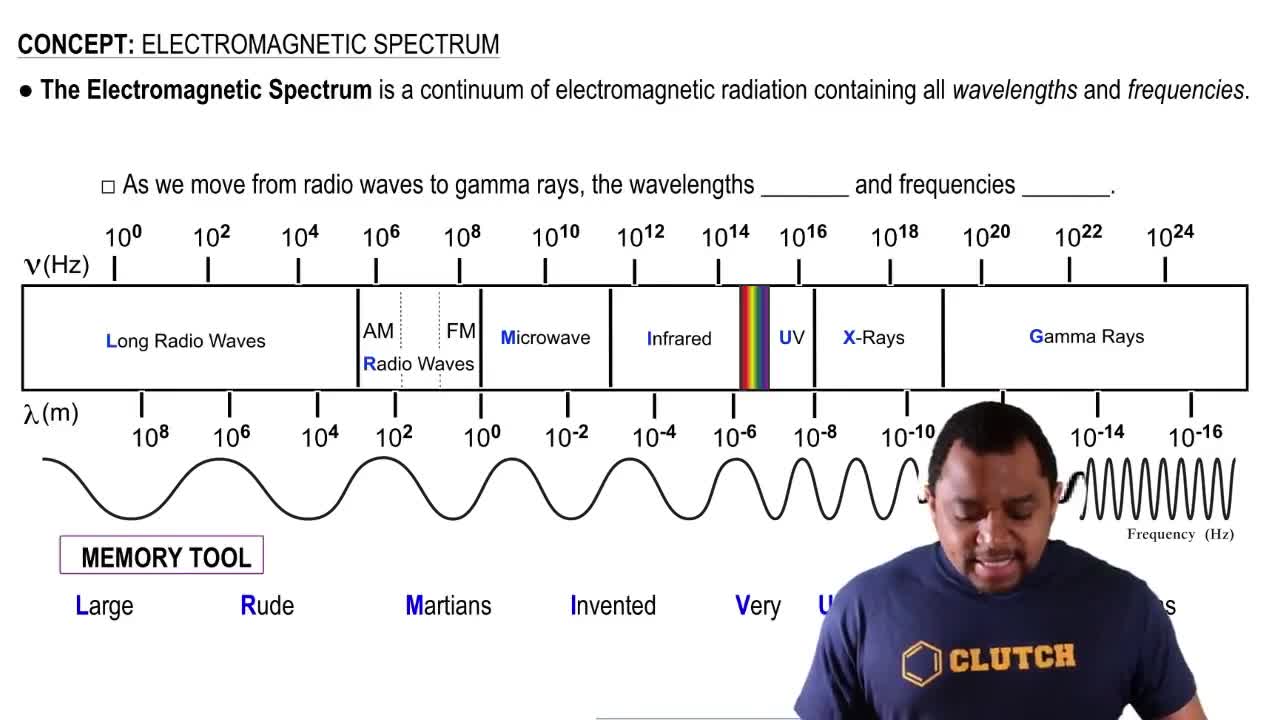
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Wavelength and Energy Relationship
The energy of electromagnetic radiation is inversely related to its wavelength, described by the equation E = hc/λ, where E is energy, h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and λ is the wavelength. Shorter wavelengths correspond to higher energy photons, while longer wavelengths correspond to lower energy. This relationship is essential for determining the energy associated with the absorption of light by atoms.
Recommended video:
Guided course
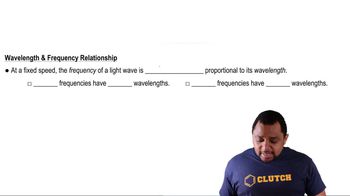
Frequency-Wavelength Relationship
Infrared Region
The infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum typically ranges from about 700 nm to 1 mm in wavelength. The absorption of light at 1094 nm indicates that this wavelength falls within the infrared range. This region is significant in various applications, including thermal imaging and spectroscopy, as it relates to molecular vibrations and transitions.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Visible Light Spectrum
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
One of the emission lines of the hydrogen atom has a wavelength of 94.974 nm. (a) In what region of the electromagnetic spectrum is this emission found?
2
views
Textbook Question
One of the emission lines of the hydrogen atom has a wavelength of 94.974 nm. (b) Determine the initial and final values of n associated with this emission.
1
views
Textbook Question
The hydrogen atom can absorb light of wavelength 1094 nm. (b) Determine the final value of n associated with this absorption.
Textbook Question
Order the following transitions in the hydrogen atom from smallest to largest frequency of light absorbed: n = 3 to n = 7, n = 4 to n = 8, n = 2 to n = 5, and n = 1 to n = 3.
1
views
Textbook Question
Write the electron configurations for the following ions, anddetermine which have noble-gas configurations:(a) Ti2+(b) Br-(c) Mg2+(d) Po2-(e) Pt2+(f) V3+
