In some applications nickel–cadmium batteries have been replaced by nickel–zinc batteries. The overall cell reaction for this relatively new battery is: 2 H2O(l) + 2 NiO(OH)(s) + Zn(s) → 2 Ni(OH)2(s) + Zn(OH)2(s) (c) A single nickel–cadmium cell has a voltage of 1.30 V. Based on the difference in the standard reduction potentials of Cd2+ and Zn2+, what voltage would you estimate a nickel–zinc battery will produce? (d) Would you expect the specific energy density of a nickel–zinc battery to be higher or lower than that of a nickel–cadmium battery?

(a) Suppose that an alkaline battery was manufactured using cadmium metal rather than zinc. What effect would this have on the cell emf?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Electrochemical Cells
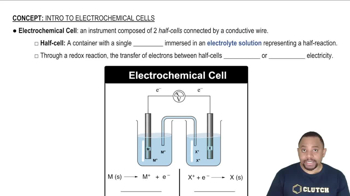
Standard Electrode Potentials

Nernst Equation

Heart pacemakers are often powered by lithium–silver chromate 'button' batteries. The overall cell reaction is 2 Li(s) + Ag2CrO4(s) → Li2CrO4(s) + 2 Ag(s) (a) Lithium metal is the reactant at one of the electrodes of the battery. Is it the anode or the cathode?
Heart pacemakers are often powered by lithium–silver chromate 'button' batteries. The overall cell reaction is 2 Li(s) + Ag2CrO4(s) → Li2CrO4(s) + 2 Ag(s) (b) Choose the two half-reactions from Appendix E that most closely approximate the reactions that occur in the battery. What standard emf would be generated by a voltaic cell based on these half-reactions?
In some applications nickel–cadmium batteries have been replaced by nickel–zinc batteries. The overall cell reaction for this relatively new battery is: 2 H2O(l) + 2 NiO(OH)(s) + Zn(s) → 2 Ni(OH)2(s) + Zn(OH)2(s) (b) What is the anode half-reaction?
