Give the chemical formula for each of the following ionic compounds: (a) sodium phosphate (b) zinc nitrate (c) barium bromate (d) iron(II) perchlorate
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 75c
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (c) H3PO4
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the elements in the given chemical formula. In H3PO4, the elements are hydrogen (H), phosphorus (P), and oxygen (O).
Recognize that the formula represents an acid because it starts with hydrogen (H).
Determine the type of acid by noting the non-hydrogen elements. Since phosphorus and oxygen are present, it is an oxyacid.
Recall the naming convention for oxyacids: if the polyatomic ion ends in '-ate', the acid name will end in '-ic'. The polyatomic ion here is phosphate (PO43-).
Apply the naming convention to name the acid as phosphoric acid.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
48sWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Acids and Their Formulas
Acids are substances that can donate protons (H⁺ ions) in a solution. The chemical formula of an acid typically starts with hydrogen, followed by the anion. For example, H₃PO₄ contains three hydrogen atoms and the phosphate ion (PO₄³⁻), indicating it is a triprotic acid capable of donating three protons.
Recommended video:
Guided course
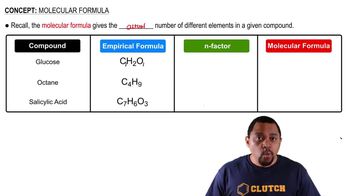
Determining Molecular Formulas
Naming Acids
The naming of acids depends on the anion present. If the anion ends in '-ate,' the acid name typically ends in '-ic,' while anions ending in '-ite' lead to names ending in '-ous.' For H₃PO₄, the anion is phosphate (PO₄³⁻), so the acid is named phosphoric acid.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Naming Binary Acids Example
Triprotic Acids
Triprotic acids are capable of donating three protons per molecule in aqueous solution. This characteristic affects their strength and behavior in chemical reactions. H₃PO₄, or phosphoric acid, is a common example, and its ability to donate multiple protons makes it important in various chemical and biological processes.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Triprotic Acid Equilibrium
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Give the chemical formula for each of the following ionic compounds: (e) cobalt(II) hydrogen carbonate (f) chromium(III) acetate (g) potassium dichromate.
Textbook Question
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (b) HBr
Textbook Question
Give the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (d) hypochlorous acid (e) iodic acid (f) sulfurous acid.
Textbook Question
Provide the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (a) hydroiodic acid (b) chloric acid (c) nitrous acid
Textbook Question
Provide the name or chemical formula, as appropriate, for each of the following acids: (e) HClO4
