Textbook Question
(a) What is a hydrocarbon?

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
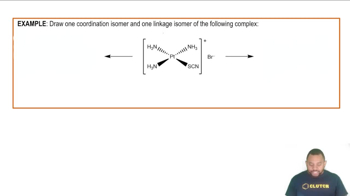
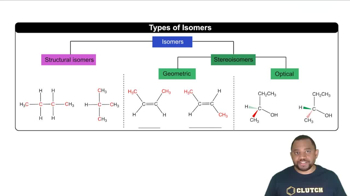
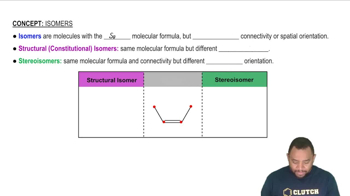
(a) What is a hydrocarbon?
(b) Pentane is the alkane with a chain of five carbon atoms. Determine its molecular formula.
(b) Pentane is the alkane with a chain of five carbon atoms. Determine its empirical formula.
(b) Among the four alkanes, ethane, propane, butane, and pentane, which is capable of existing in isomeric forms?
(a) What is a functional group?
(b) What functional group characterizes an alcohol?