Write the chemical formula for each substance mentioned in the following word descriptions (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (b) On treatment with hydrofluoric acid, silicon dioxide forms silicon tetrafluoride and water. (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (c) Sulfur dioxide reacts with water to form sulfurous acid. (use the front inside cover to find the symbols for the elements you do not know). (d) The substance phosphorus trihydride, commonly called phosphine, is a toxic gas. (e) Perchloric acid reacts with cadmium to form cadmium(II) perchlorate.
Ch.2 - Atoms, Molecules, and Ions

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 2, Problem 81a
(a) What is a hydrocarbon?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Understand that a hydrocarbon is an organic compound composed exclusively of hydrogen and carbon atoms.
Recognize that hydrocarbons are the simplest type of organic molecules and serve as the backbone for many other organic compounds.
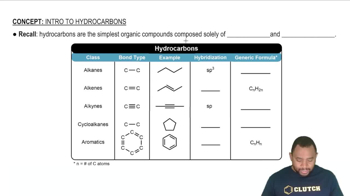
Know that hydrocarbons can be classified into different types based on the types of bonds between carbon atoms, such as alkanes (single bonds), alkenes (one or more double bonds), and alkynes (one or more triple bonds).
Be aware that hydrocarbons can be either saturated (only single bonds) or unsaturated (containing double or triple bonds).
Remember that hydrocarbons are important as fuels and raw materials in the chemical industry.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
1mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Definition of Hydrocarbon
A hydrocarbon is an organic compound composed exclusively of hydrogen and carbon atoms. These compounds form the basis of many fuels and organic materials, and their properties depend on the types of bonds and structures present.
Recommended video:
Guided course
Intro To Hydrocarbons
Types of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are classified into alkanes (single bonds), alkenes (one or more double bonds), alkynes (one or more triple bonds), and aromatic hydrocarbons (ring structures). Each type has distinct chemical and physical properties.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro To Hydrocarbons
Importance of Hydrocarbons
Hydrocarbons are fundamental in chemistry and industry as fuels, solvents, and raw materials for plastics and other chemicals. Understanding their structure helps explain their reactivity and uses.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Intro To Hydrocarbons
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Assume that you encounter the following sentences in your reading. What is the chemical formula for each substance mentioned? (c) Hydrogen cyanide is a very poisonous gas.
Textbook Question
(b) Pentane is the alkane with a chain of five carbon atoms. Determine its molecular formula.
Textbook Question
(b) Pentane is the alkane with a chain of five carbon atoms. Determine its empirical formula.
Textbook Question
(a) What is meant by the term isomer?
