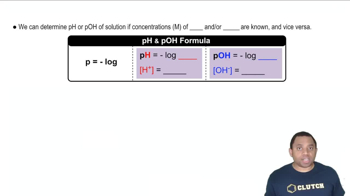
Textbook Question
A sample of 0.1687 g of an unknown monoprotic acid was dissolved in 25.0 mL of water and titrated with 0.1150 M NaOH. The acid required 15.5 mL of base to reach the equivalence point. (b) After 7.25 mL of base had been added in the titration, the pH was found to be 2.85. What is the Ka for the unknown acid?