Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the reaction of each of the following bases with water: (a) propylamine, C3H7NH2
Ch.16 - Acid-Base Equilibria

Brown14th EditionChemistry: The Central ScienceISBN: 9780134414232Not the one you use?Change textbook
Chapter 16, Problem 71
Calculate the molar concentration of OH- in a 0.075 M solution of ethylamine (C2H5NH2); Kb = 6.4 * 10^-4. Calculate the pH of this solution.
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the reaction: Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is a weak base and will react with water to form C2H5NH3+ and OH-. Write the equilibrium expression for this reaction.
Write the expression for the base dissociation constant (Kb): Kb = [C2H5NH3+][OH-] / [C2H5NH2].
Set up an ICE (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) table to determine the concentrations of the species at equilibrium. Assume the initial concentration of OH- and C2H5NH3+ is 0, and the change in concentration for C2H5NH2 is -x, for OH- and C2H5NH3+ is +x.
Substitute the equilibrium concentrations from the ICE table into the Kb expression: Kb = (x)(x) / (0.075 - x).
Solve for x, which represents the concentration of OH- at equilibrium. Use the approximation method if x is small compared to the initial concentration, then calculate the pH using the relation pH = 14 - pOH, where pOH = -log[OH-].
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Base Ionization and Kb
Ethylamine (C2H5NH2) is a weak base that partially ionizes in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH-) and its conjugate acid (C2H5NH3+). The base dissociation constant (Kb) quantifies the extent of this ionization, with a higher Kb indicating a stronger base. In this case, Kb = 6.4 x 10^-4 helps determine the concentration of OH- produced in the solution.
Recommended video:
Guided course
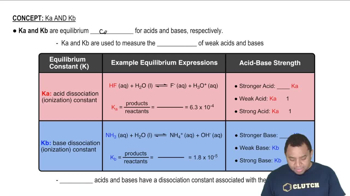
Characteristics of Ka and Kb
Equilibrium Concentrations
To find the concentration of OH- in the solution, we set up an equilibrium expression based on the ionization of ethylamine. Using an ICE (Initial, Change, Equilibrium) table, we can express the changes in concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium. This allows us to solve for the concentration of OH- using the Kb value.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Thermal Equilibrium
pH and pOH Calculations
The pH of a solution is a measure of its acidity, while pOH measures its basicity. They are related through the equation pH + pOH = 14. Once the concentration of OH- is determined, the pOH can be calculated using the formula pOH = -log[OH-]. Subsequently, the pH can be found by rearranging the equation to pH = 14 - pOH.
Recommended video:
Guided course
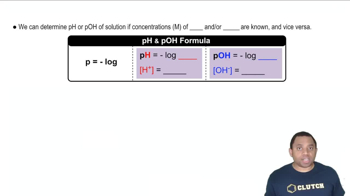
pH and pOH Calculations
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Write the chemical equation and the Kb expression for the reaction of each of the following bases with water: (c) benzoate ion, C6H5CO2-
Textbook Question
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (a) What are the equilibrium concentrations of C10H15ON, C10H15ONH+, and OH-?
Textbook Question
Ephedrine, a central nervous system stimulant, is used in nasal sprays as a decongestant. This compound is a weak organic base: C10H15ON1aq2 + H2O1l2 Δ C10H15ONH+1aq2 + OH-1aq2 A 0.035 M solution of ephedrine has a pH of 11.33. (b) Calculate Kb for ephedrine.
