Use the phase diagram of neon to answer the following questions. (a) What is the approximate value of the normal boiling point?

In terms of the arrangement and freedom of motion of the molecules, how are the nematic liquid crystalline phase and an ordinary liquid phase similar? How are they different?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Molecular Arrangement

Freedom of Motion

Phase Behavior
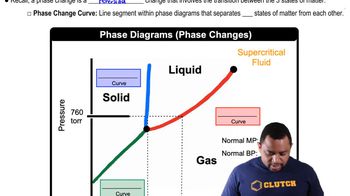
Use the phase diagram of neon to answer the following questions. (b) What can you say about the strength of the intermolecular forces in neon and argon based on the critical points of Ne and Ar (see Table 11.5.)?
At 25 °C gallium is a solid with a density of 5.91 g/cm3. Its melting point, 29.8 °C, is low enough that you can melt it by holding it in your hand. The density of liquid gallium just above the melting point is 6.1 g/cm3. Based on this information, what unusual feature would you expect to find in the phase diagram of gallium?
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) The liquid crystal state is another phase of matter, just like solid, liquid, and gas. (b) Liquid crystalline molecules are generally spherical in shape. (d) Molecules that exhibit a liquid crystalline phase show weaker-than-expected intermolecular forces. (e) Molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen are likely to form liquid crystalline phases. (f) Molecules can exhibit more than one liquid crystalline phase.
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (c) Molecules that exhibit a liquid crystalline phase do so at well-defined temperatures and pressures.
