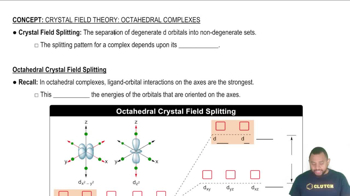
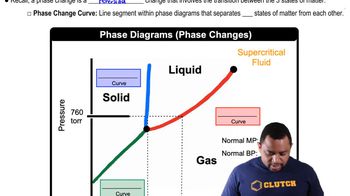
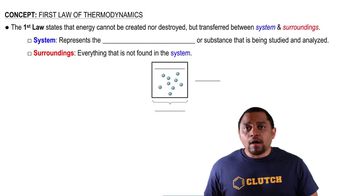
Textbook Question
Indicate whether each statement is true or false: (a) The liquid crystal state is another phase of matter, just like solid, liquid, and gas. (b) Liquid crystalline molecules are generally spherical in shape. (d) Molecules that exhibit a liquid crystalline phase show weaker-than-expected intermolecular forces. (e) Molecules containing only carbon and hydrogen are likely to form liquid crystalline phases. (f) Molecules can exhibit more than one liquid crystalline phase.