Textbook Question
List the three states of matter in order of (b) increasing intermolecular attraction.
3
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
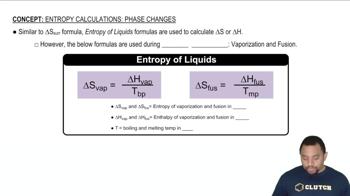
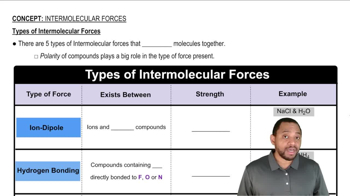
List the three states of matter in order of (b) increasing intermolecular attraction.
(a) How does the average kinetic energy of molecules com- pare with the average energy of attraction between mole- cules in solids, liquids, and gases?
(c) What happens to a gas if you put it under extremely high pressure?
At room temperature, Si is a solid, CCl4 is a liquid, and Ar is a gas. List these substances in order of (a) increasing intermolecular energy of attraction