Phase Changes
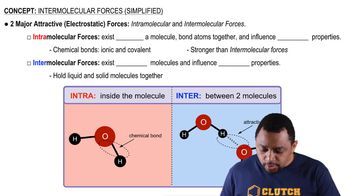
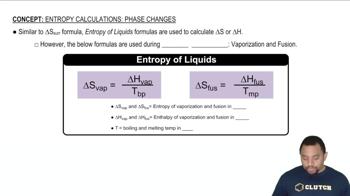
Phase changes refer to the transitions between solid, liquid, and gas states, which occur due to changes in temperature and pressure. During these changes, the balance between kinetic energy and intermolecular forces shifts, affecting the average energy of attraction. For instance, as a solid melts into a liquid, the kinetic energy increases, overcoming some intermolecular forces, which is essential for understanding the energy dynamics in different phases.

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance