Textbook Question
(a) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates between all molecules?
3
views

 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance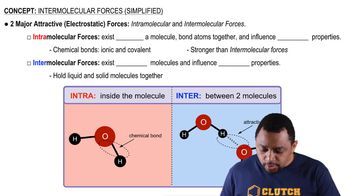


(a) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates between all molecules?
(b) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates only between polar molecules?
(c) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates only between the hydrogen atom of a polar bond and a nearby small electronegative atom?
(b) Which of these kinds of interactions are broken when a liquid is converted to a gas?
Describe the intermolecular forces that must be overcome to convert these substances from a liquid to a gas: (a) SO2, (b) CH3COOH, (c) H2S.
Which type of intermolecular force accounts for each of these differences? (a) CH3OH boils at 65 °C; CH3SH boils at 6 °C. (d) Acetone boils at 56 °C, whereas 2-methylpropane boils at -12 °C.