(b) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates only between polar molecules?

(b) Which of these kinds of interactions are broken when a liquid is converted to a gas?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance
Verified video answer for a similar problem:
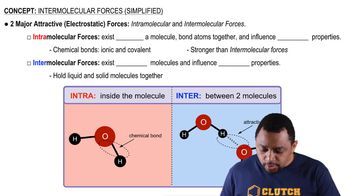
Key Concepts
Intermolecular Forces
Phase Change
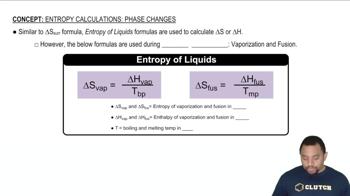
Vaporization
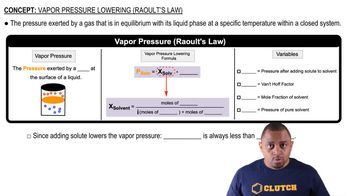
(c) Which type of intermolecular attractive force operates only between the hydrogen atom of a polar bond and a nearby small electronegative atom?
Describe the intermolecular forces that must be overcome to convert these substances from a liquid to a gas: (a) SO2, (b) CH3COOH, (c) H2S.
Which type of intermolecular force accounts for each of these differences? (a) CH3OH boils at 65 °C; CH3SH boils at 6 °C. (d) Acetone boils at 56 °C, whereas 2-methylpropane boils at -12 °C.
Which type of intermolecular force accounts for each of these differences? (b) Xe is a liquid at atmospheric pressure and 120 K, whereas Ar is a gas under the same conditions. (c) Kr, atomic weight 84 amu, boils at 120.9 K, whereas Cl2, molecular weight about 71 amu, boils at 238 K.
