Table 10.3 shows that the van der Waals b parameter has units of L/mol. This means that we can calculate the sizes of atoms or molecules from the b parameter. Refer back to the discussion in Section 7.3. Is the van der Waals radius we calculate from the b parameter of Table 10.3 more closely associated with the bonding or nonbonding atomic radius discussed there? Explain.

A 6.0-L tank is filled with helium gas at a pressure of 2 MPa. How many balloons (each 2.00 L) can be inflated to a pressure of 101.3 kPa, assuming that the temperature remains constant and that the tank cannot be emptied below 101.3 kPa?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidanceKey Concepts
Ideal Gas Law

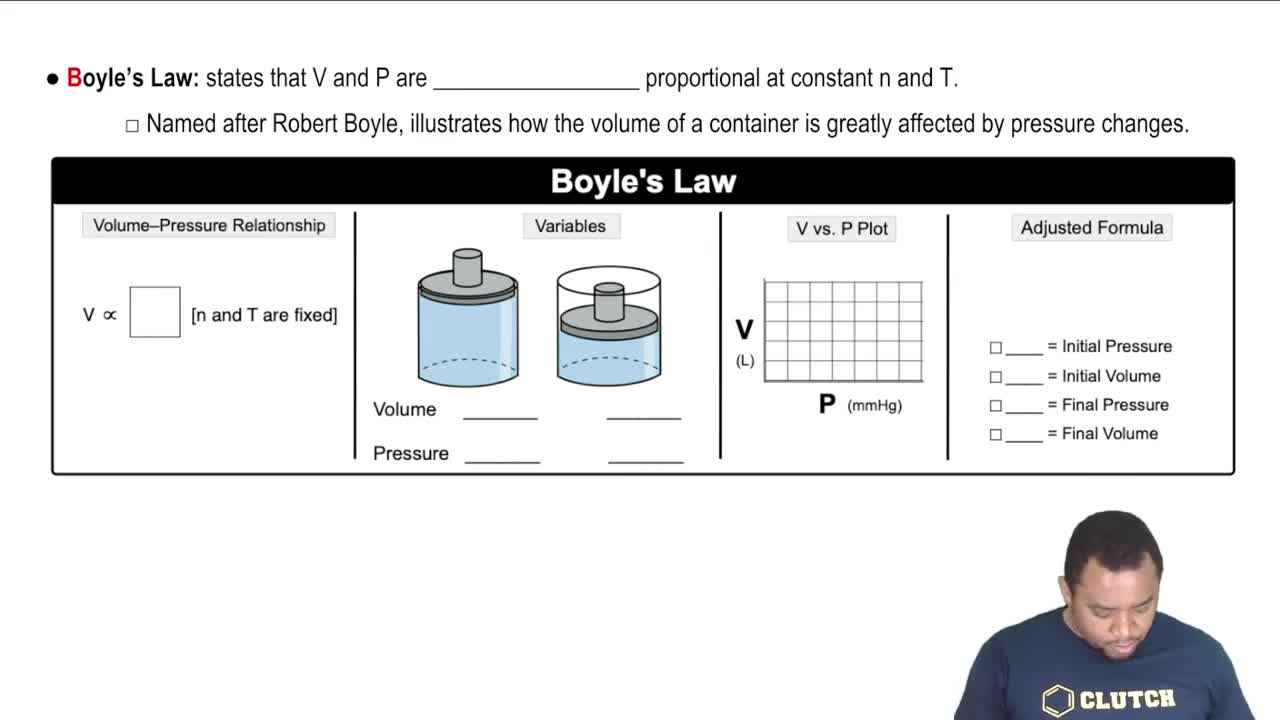
Boyle's Law
Gas Stoichiometry

A gas bubble with a volume of 1.0 mm3 originates at the bottom of a lake where the pressure is 3.0 atm. Calculate its volume when the bubble reaches the surface of the lake where the pressure is 730 torr, assuming that the temperature does not change.
Carbon dioxide, which is recognized as the major contributor to global warming as a 'greenhouse gas,' is formed when fossil fuels are combusted, as in electrical power plants fueled by coal, oil, or natural gas. One potential way to reduce the amount of CO2 added to the atmosphere is to store it as a compressed gas in underground formations. Consider a 1000-megawatt coal-fired power plant that produces about 6×106 tons of CO2 per year. (a) Assuming ideal-gas behavior, 101.3 kPa, and 27 °C, calculate the volume of CO2 produced by this power plant.
Carbon dioxide, which is recognized as the major contributor to global warming as a “greenhouse gas,” is formed when fossil fuels are combusted, as in electrical power plants fueled by coal, oil, or natural gas. One potential way to reduce the amount of CO2 added to the atmosphere is to store it as a compressed gas in underground formations. Consider a 1000-megawatt coal-fired power plant that produces about 6⨉106 tons of CO2 per year. (b) If the CO2 is stored underground as a liquid at 10 C and 12.16 MPa and a density of 1.2 g/cm3, what volume does it possess?
