Using the molecular orbital energy ordering for second-row homonuclear diatomic molecules in which the π2p orbitals lie at higher energy than the σ2p, draw MO energy diagrams and predict the bond order in a molecule or ion with each number of total valence electrons. Will the molecule or ion be diamagnetic or paramagnetic? d. 14
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory

All textbooks Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 79
Problem 79
 Tro 4th Edition
Tro 4th Edition Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory
Ch.10 - Chemical Bonding II: Molecular Shapes & Valence Bond Theory Problem 79
Problem 79Chapter 10, Problem 79
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond order? C2, C2+ , C2- According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond energy? According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the shortest bond length?
 Verified step by step guidance
Verified step by step guidance1
Identify the molecular orbitals (MOs) for each species: C_2, C_2^+, and C_2^-.
Determine the electron configuration for each species using the MO diagram for diatomic carbon species.
Calculate the bond order for each species using the formula: Bond Order = (Number of bonding electrons - Number of antibonding electrons) / 2.
Compare the bond orders to determine which species has the highest bond order, as bond order is directly related to bond energy and inversely related to bond length.
Conclude that the species with the highest bond order will have the highest bond energy and the shortest bond length.

Verified video answer for a similar problem:
This video solution was recommended by our tutors as helpful for the problem above.
Video duration:
11mWas this helpful?
Key Concepts
Here are the essential concepts you must grasp in order to answer the question correctly.
Molecular Orbital (MO) Theory
Molecular Orbital Theory describes the behavior of electrons in molecules by combining atomic orbitals to form molecular orbitals. These orbitals can be occupied by electrons and are classified as bonding, antibonding, or non-bonding. The arrangement of electrons in these orbitals determines properties such as bond order, bond energy, and bond length.
Recommended video:
Guided course
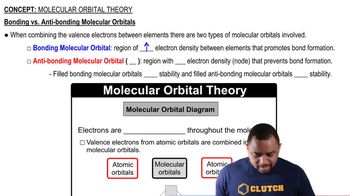
Molecular Orbital Theory
Bond Order
Bond order is a measure of the number of chemical bonds between a pair of atoms. It is calculated as the difference between the number of bonding and antibonding electrons divided by two. A higher bond order indicates a stronger bond and is associated with greater stability and shorter bond lengths.
Recommended video:
Guided course

Average Bond Order
Bond Energy
Bond energy is the amount of energy required to break a bond between two atoms in a molecule. It is directly related to bond order; higher bond orders typically correspond to higher bond energies. This concept is crucial for understanding the stability of molecules and the energy changes during chemical reactions.
Recommended video:
Guided course
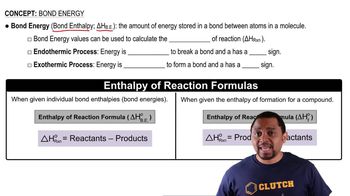
Bond Energy
Related Practice
Textbook Question
Textbook Question
Use molecular orbital theory to predict if each molecule or ion exists in a relatively stable form. a. H22- b. Ne2 c. He22+ d. F22-
Textbook Question
Apply molecular orbital theory to predict if each molecule or ion exists in a relatively stable form. a. C22+ b. Li2 c. Be22+ d. Li22-
Textbook Question
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond order? O2, O2- , O22-
Textbook Question
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the highest bond energy? O2, O2- , O22-
Textbook Question
According to MO theory, which molecule or ion has the shortest bond length? O2, O2- , O22-
1
views